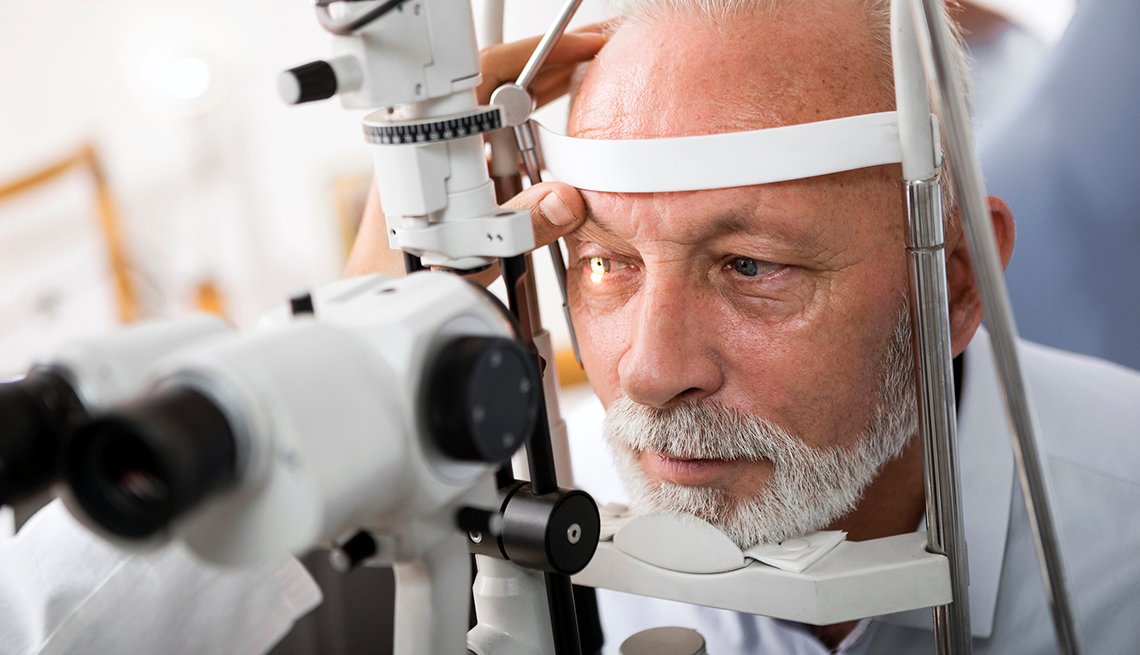
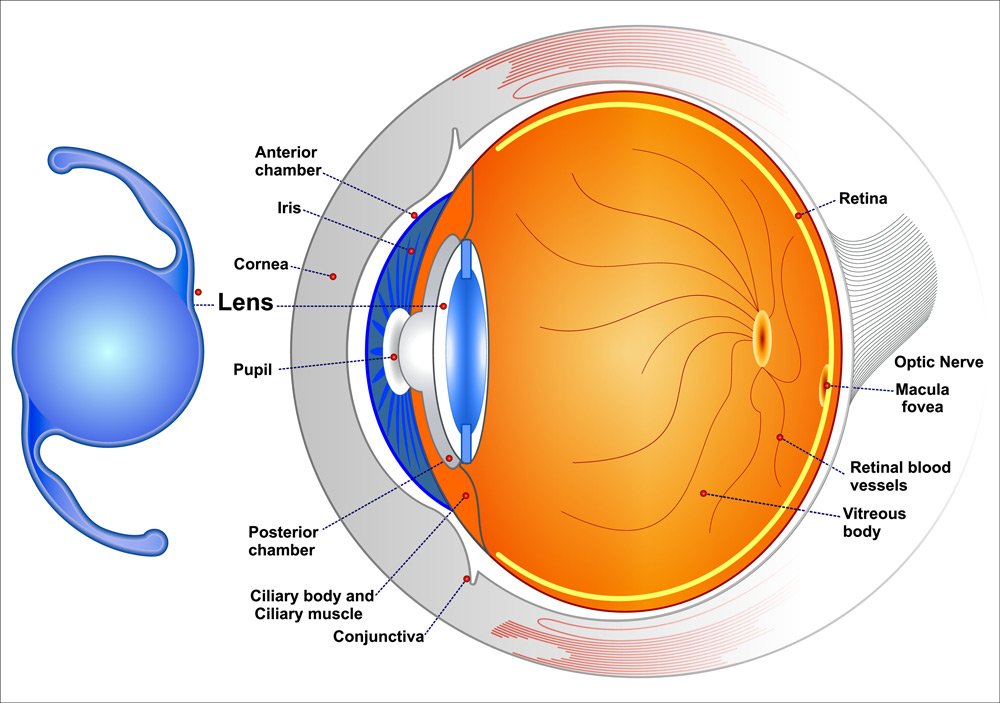
Cataract Eye Surgery
Cataract
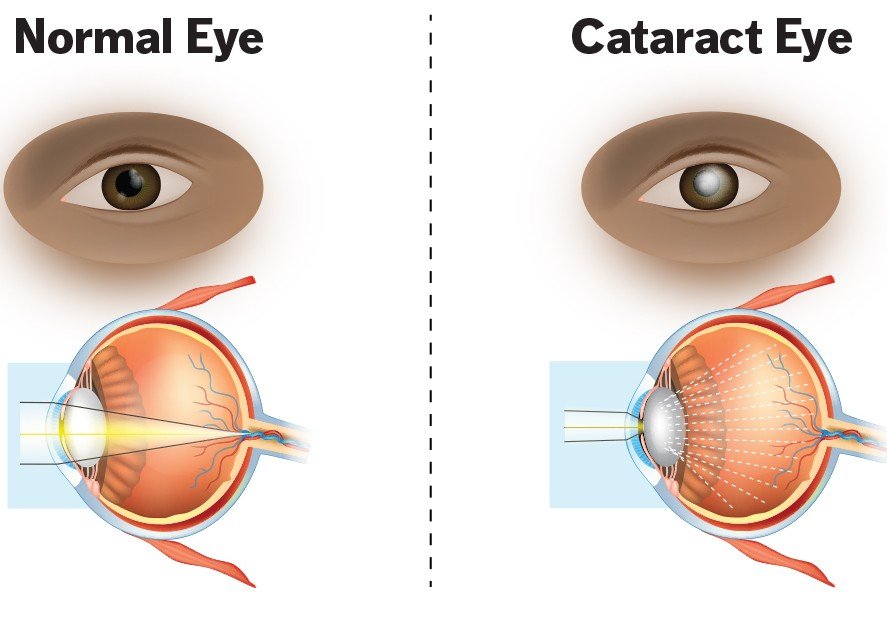
What Is a Cataract?
 SYMPTOMS OF CATARACTS
SYMPTOMS OF CATARACTS
 Blurry vision
Blurry vision  Trouble seeing at night
Trouble seeing at night  Seeing colors as faded
Seeing colors as faded  Increased sensitivity to glare
Increased sensitivity to glare  Halos surrounding lights
Halos surrounding lights  Double vision in the affected eye.
Double vision in the affected eye.  Aneed for frequent changes in prescription glasses
Aneed for frequent changes in prescription glasses  WHAT CAUSES CATARACTS ?
WHAT CAUSES CATARACTS ?
 An overproduction of oxidants, which are oxygen molecules that have been chemically altered due to normal daily life
An overproduction of oxidants, which are oxygen molecules that have been chemically altered due to normal daily life  Smoking
Smoking  Ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation  The long-term use of steroids and other medications
The long-term use of steroids and other medications  Certain diseases, such as diabetes
Certain diseases, such as diabetes  Trauma
Trauma  Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy  TYPES OF CATARACTS
TYPES OF CATARACTS
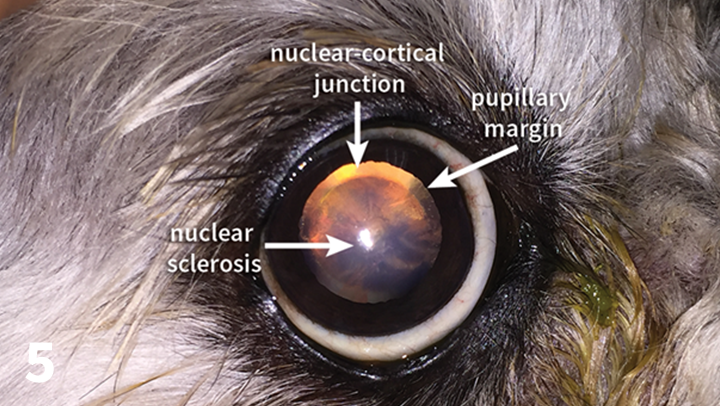
Nuclear cataracts
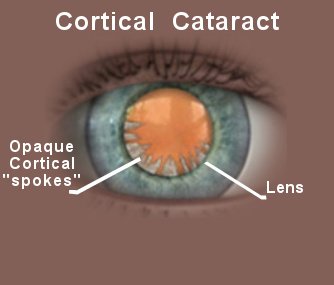
Cortical cataracts
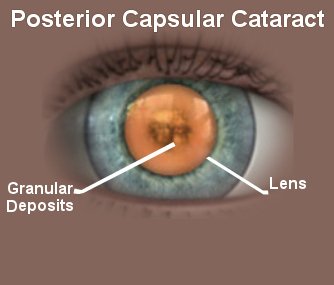
Posterior capsular
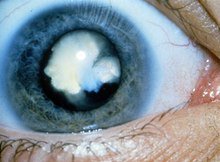
Congenital cataracts
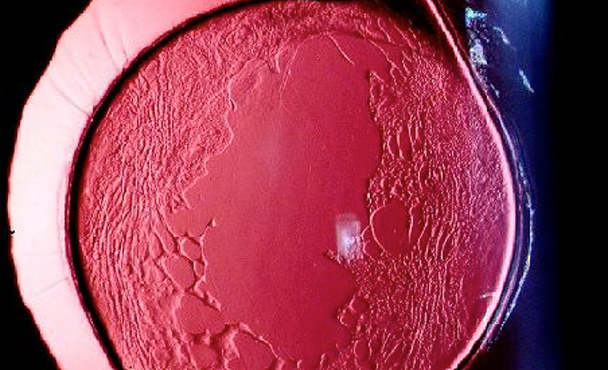
Secondary cataracts
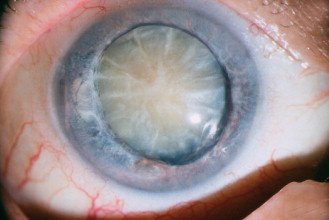
Traumatic cataracts
Radiation cataracts
 RISK FACTORS OF CATARACTS
RISK FACTORS OF CATARACTS

OLDER AGE

HEAVY ALCOHOL USE

SMOKING

OBESITY

HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE

PREVIOUS EYE INJURIES

A FAMILY HISTORY OF CATARACTS

TOO MUCH SUN EXPOSURE

DIABETES

EXPOSURE TO RADIATION
 DIAGNOSING CATARACTS
DIAGNOSING CATARACTS
 TREATMENT
TREATMENT
Treatment
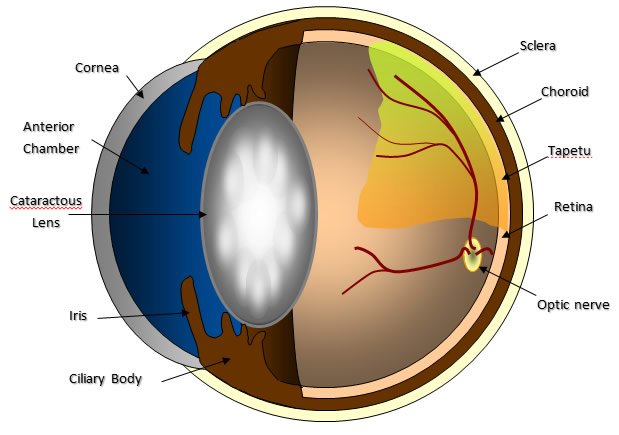
There are numerous types of IOL (Intraocular lens) option that we use to replace the original one.

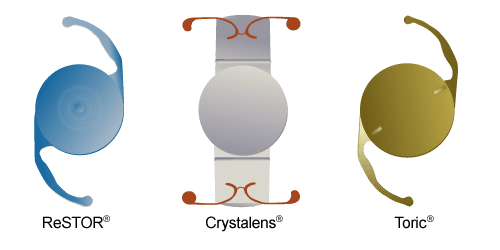
 PREMIUM MONOFOCAL IOL (ASPHERIC IOLS)
PREMIUM MONOFOCAL IOL (ASPHERIC IOLS)
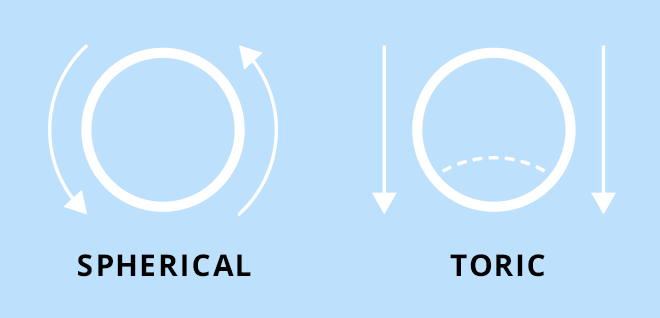
 TORIC IOLS
TORIC IOLS
 MULTIFOCAL IOLS
MULTIFOCAL IOLS
 WHICH PATIENTS ARE SUITABLE FOR THIS SURGERY?
WHICH PATIENTS ARE SUITABLE FOR THIS SURGERY?The most suitable patient is the one who strongly desires not to wear glasses after having eliminated medical contra-indications and exposed side eff ects especially halos.
Patients with significant night activity should be avoided as halos at night may disturb patients especially when driving.
These halos disappear for 20% of patients during the first month and for 40% of patients during the first year presumably by a Neuro-adaptation phenomenon.
They persist to varying degrees for the remaining 40% without significant reduction in activities.
 WHICH PREOPERATIVE ASSESSMENT?
WHICH PREOPERATIVE ASSESSMENT?An orthoptic assessment will be done to eliminate any microtropia. Analysis of the cornea must be scrupulous and any disease of the tear film must be treated beforehand because meibomian gland dysfunction can greatly disturb patients postoperatively.
New apodized diffractive IOLs being pupil-dependent, photopic (Scheimpflug data) and mesopic (Colvard Pupillometer) measurement of the pupil will avoid narrow photopic or over dilated scotopic pupils.
Limits of 2mm in photopic and 5 mm in scotopic will avoid any pupillary refractive disorder postoperatively.
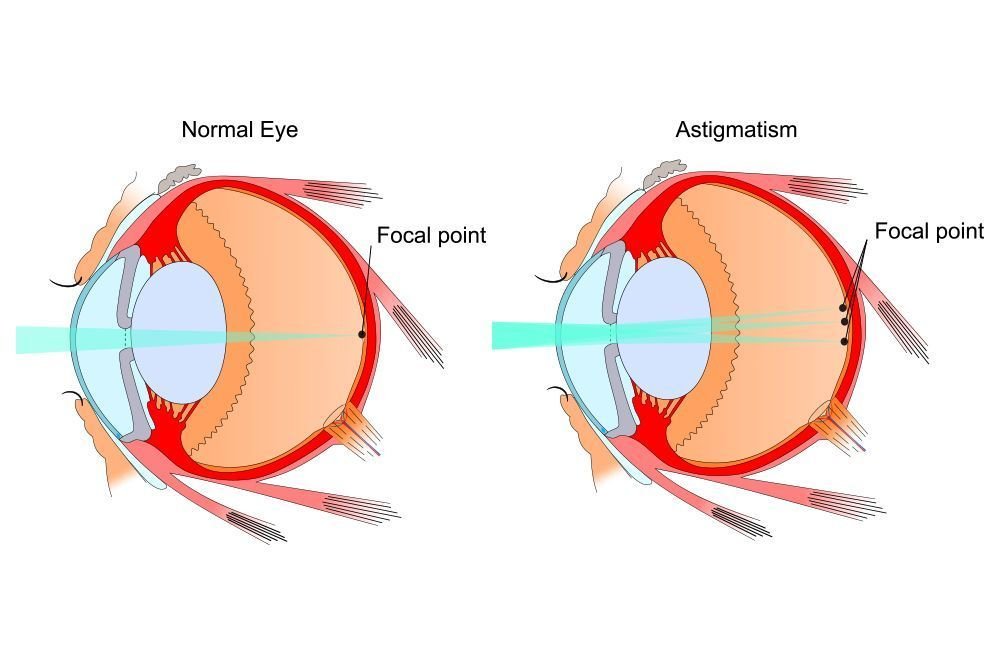
Astigmatism management is of paramount importance for obtaining ideal postoperative results with MFIOLs. A postoperative astigmatic error exceeding three-quarters of a diopter results in significant decline in visual quality.
A residual astigmatism lower than 0.50D does not seem to impair visual acuity, but we systematically treat astigmatism with toric lens if possible with the goal of no residual astigmatism.
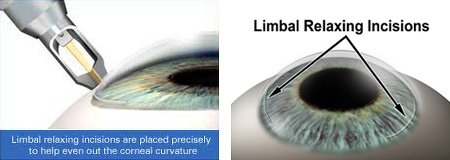
Corneal limbal incisions could be performing to treat lower astigmatism.
Pathological capsular bags or capsular bags at risk because of uncontrolled healing should be avoided in order to prevent any decentration of these IOLs.
Finally a macular OCT analysis is performed when there is a doubt at fund us examination in order to eliminate an incipient macular traction syndrome or Epiretinal Membrane (ERM)
 TYPES OF MULTIFOCAL INTRAOCULAR LENSES
TYPES OF MULTIFOCAL INTRAOCULAR LENSES
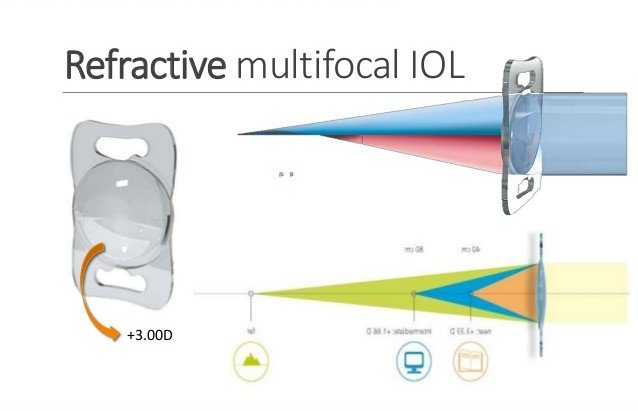
Refractive IOLs
Diffractive IOLs
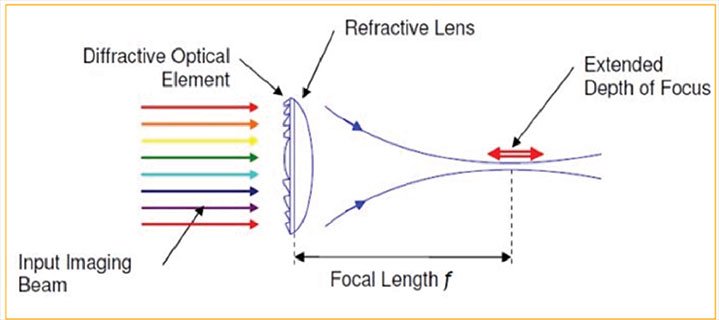
Extended depth of focus (EDOF) IOLs
 WHICH SURGICAL TECHNIQUE?
WHICH SURGICAL TECHNIQUE?
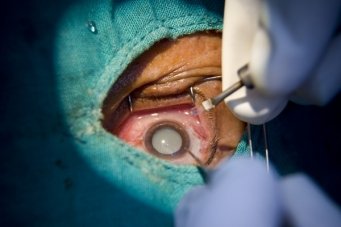
 OUTLOOK OF A CATARACT
OUTLOOK OF A CATARACT
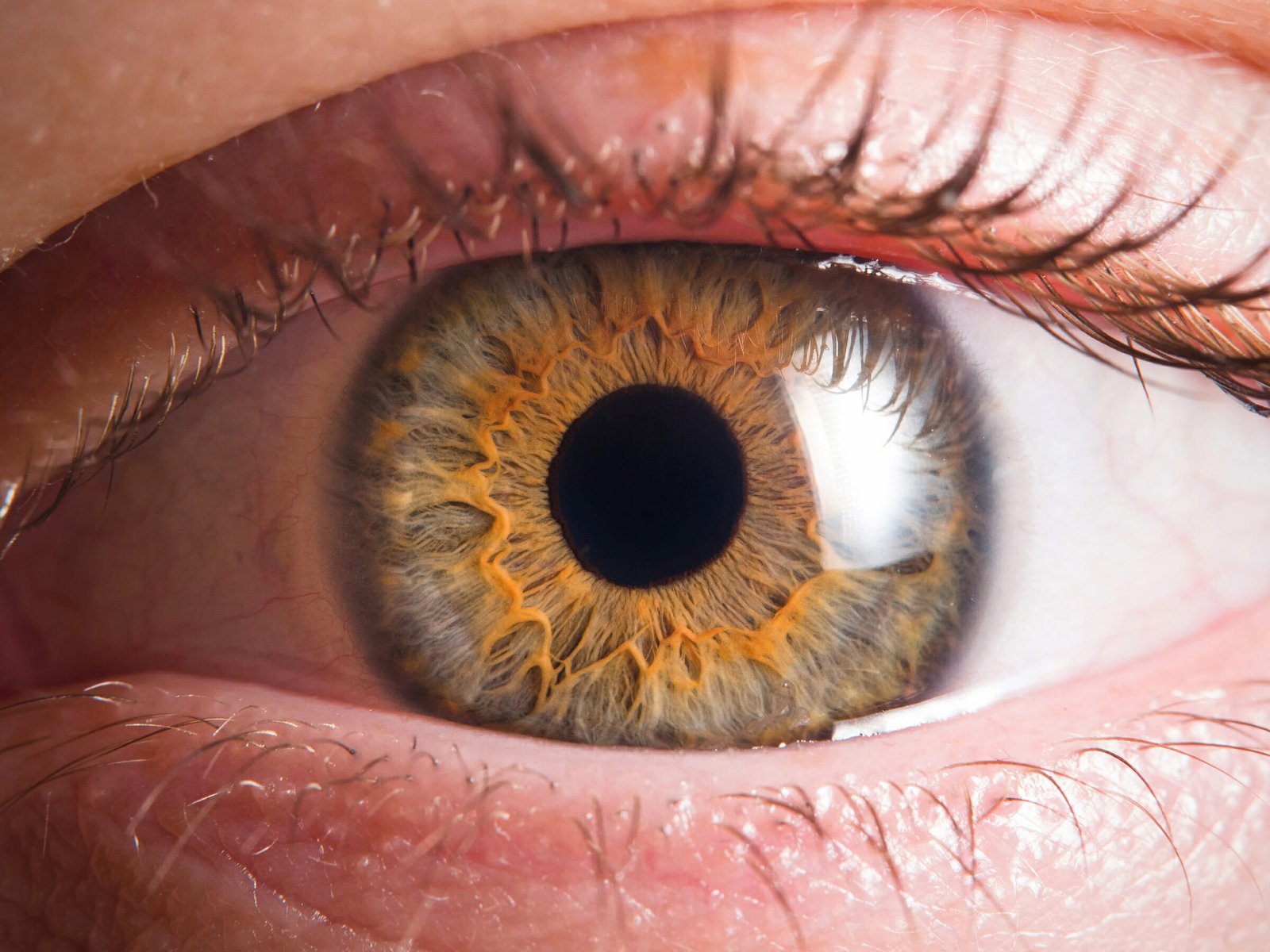
 PREVENTION OF CATARACTS
PREVENTION OF CATARACTS
 Protect your eyes from UVB rays by wearing sunglasses outside
Protect your eyes from UVB rays by wearing sunglasses outside  Have regular eye exams
Have regular eye exams  Stop smoking
Stop smoking  Eat fruits and vegetables that contain antioxidants
Eat fruits and vegetables that contain antioxidants  Double vision in the affected eye.
Double vision in the affected eye.  Keep diabetes and other medical conditions in check
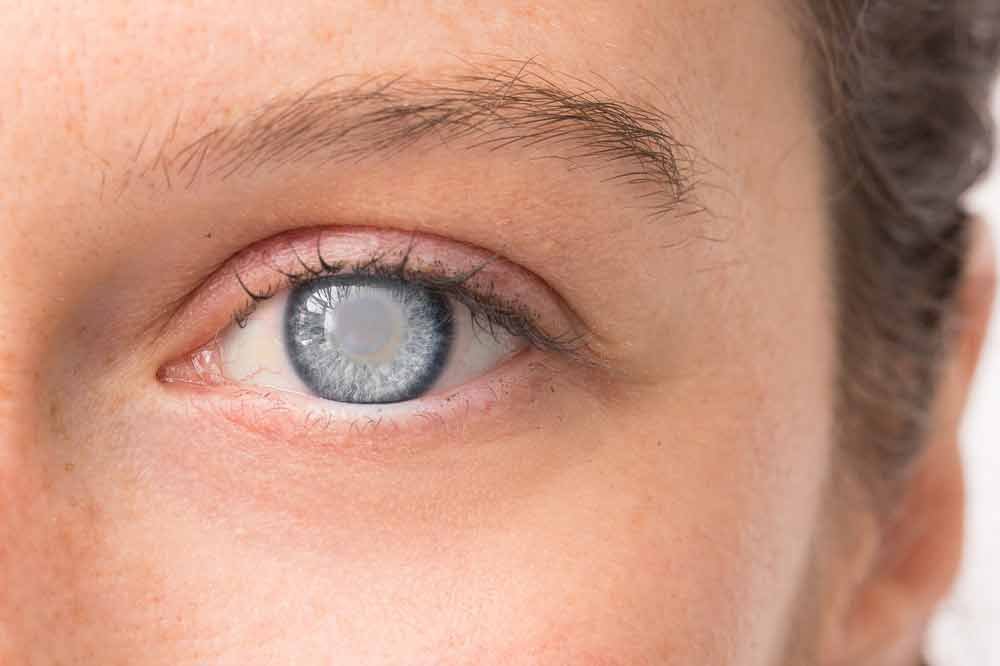
Keep diabetes and other medical conditions in check  7 SYMPTOMS OF CATARACTS
7 SYMPTOMS OF CATARACTS
- Too much time in the sun without eye protection
- Smoking
- High blood sugar
- Using steroid medications
- Exposure to radiation

- Posterior subcapsular cataracts
- Nuclear cataracts in the center of the lens
- Cortical cataracts on the side of the lens, which appear as small streaks






- brain tumor
- corneal swelling
- multiple sclerosis
- stroke, cataracts
- brain injury
- uncontrolled diabetes or hypertension
- Graves’ disease
- myasthenia gravis
 SEE YOUR DOCTOR
SEE YOUR DOCTOR